The Role of LGSF in Disaster-Resistant Buildings
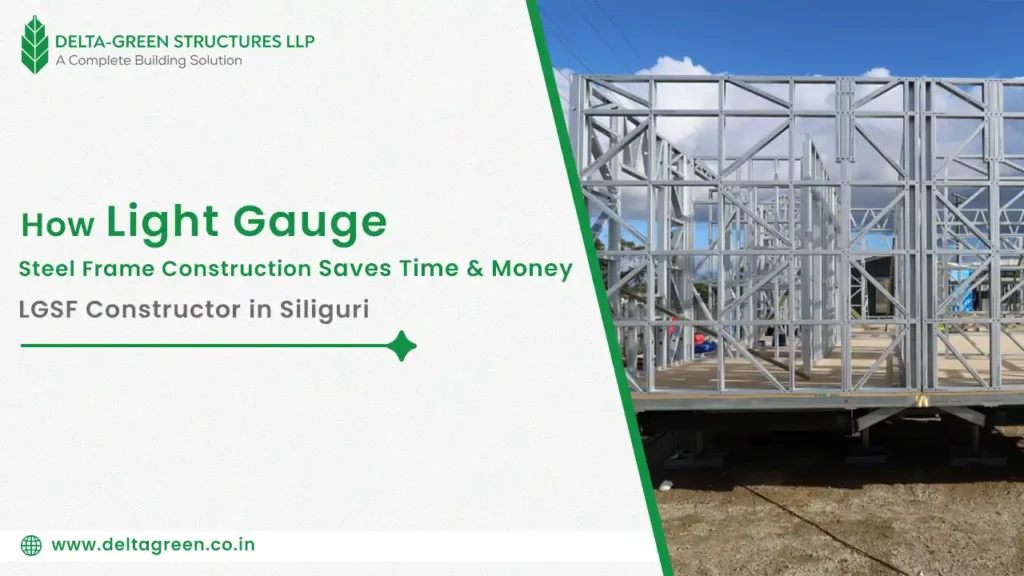
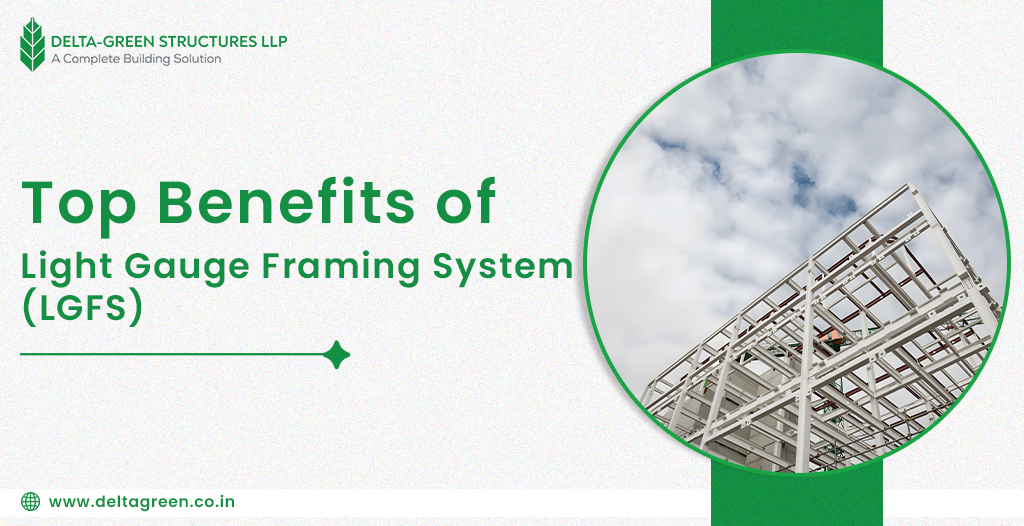
Living in West Bengal, we understand the power of nature. From the fierce cyclones born in the Bay of Bengal to the ever-present seismic rumbles and the devastating floods that follow heavy rains, the need for safe, resilient housing and buildings isn’t just a preference – it’s a necessity. At Delta Green Structure, as a leading LGSF manufacturer in West Bengal, we believe everyone deserves a home or workplace that stands strong when nature unleashes its fury. That’s where Light Gauge Steel Framing (LGSF) isn’t just an alternative construction method; it’s a powerful shield against disasters. Why Traditional Building Methods Often Fall Short Before diving into the LGSF advantage, let’s acknowledge the vulnerabilities often found in conventional construction prevalent in our region: Brick-and-Mortar Brittleness: Traditional brick walls, while solid under vertical loads, can be brittle. During earthquakes, they are prone to cracking and catastrophic collapse. They offer little flexibility to absorb seismic energy. Weight = Vulnerability: Heavy concrete structures exert immense downward force. On weak or water-logged soil (common in flood-prone areas), this can lead to settling or even sinking. During earthquakes, this mass translates into greater destructive force. Water Woes: Prolonged flooding, like we see in parts of West Bengal, wreaks havoc on traditional materials. Bricks absorb water, weakening the structure and leading to efflorescence. Timber rots, warps, and attracts pests. Reinforced concrete, if not perfectly sealed, can see its steel reinforcements corrode over time. Wind Weakness: High winds from cyclones create powerful uplift and lateral forces. Poorly anchored roofs can fly off, and inadequately braced walls can fail. Traditional tiled or sheet roofs are particularly vulnerable. Fire Fuel: While concrete is fire-resistant, the internal timber elements (roofs, floors, partitions) in many traditional buildings provide ready fuel for fires, which can often follow disasters like earthquakes. LGSF: The Engineered Backbone of Resilience Light Gauge Steel Framing is exactly what it sounds like: a building framework made from thin, high-strength steel sheets, cold-formed into precise shapes (studs, tracks, joists, rafters). Think of it as an incredibly strong, lightweight skeleton for your building. But it’s the inherent properties of this system that make it a champion for disaster resistance: Exceptional Strength-to-Weight Ratio Earthquake Savior: Steel is incredibly strong but significantly lighter than concrete or dense brickwork. During an earthquake, the inertial forces generated are proportional to the building’s weight. Lighter structures experience lower forces. Crucially, steel is ductile. This means it can bend and flex significantly without suddenly snapping or collapsing, allowing it to absorb and dissipate the earthquake’s destructive energy. An LGSF structure is designed to sway safely, protecting its occupants and integrity. Flood Friend: The lightweight nature of LGSF is a major asset in flood-prone zones. It exerts far less pressure on the soil below. Even if the foundation experiences some shifting or scouring due to floodwaters, the lighter superstructure is less likely to suffer catastrophic settlement or collapse compared to a heavy concrete building. Furthermore, properly designed pile foundations combined with LGSF elevate structures above flood levels effectively. Cyclone Defense: LGSF structures are inherently rigid and can be engineered to withstand extremely high wind speeds. The steel members themselves are strong, and the entire frame is securely connected using high-strength screws and bolts, creating a continuous load path. Roof trusses and wall panels are directly anchored to this robust frame and the foundation. This integrated system resists both the uplift forces trying to pull the roof off and the lateral forces pushing against the walls. Engineered metal roofing and cladding further enhance wind resistance. Flood Resilience Core: Unlike wood or brick, galvanized steel does not rot, warp, swell, or degrade when exposed to water. After a flood, once the water recedes and the building is dried out (a much faster process than with porous materials), the structural integrity of the LGSF frame remains intact. There’s no risk of structural decay or weakening over time due to water ingress. Beyond Disaster Resistance: The Delta Green Structure Advantage Choosing LGSF for disaster resilience doesn’t mean sacrificing other benefits. In fact, it enhances them: Speed of Construction: Prefabricated LGSF components arrive on site ready for rapid assembly, drastically reducing construction time compared to traditional methods. This means safer shelters or homes can be built much faster, especially crucial in post-disaster recovery scenarios. Design Flexibility: LGSF allows for versatile architectural designs without compromising structural integrity, enabling the creation of safe and aesthetically pleasing spaces. Sustainability: Steel is the world’s most recycled material. LGSF construction generates minimal waste on-site. Precision manufacturing reduces material usage. The resulting buildings are energy-efficient, especially when combined with high-performance insulation (like PUF or Rockwool panels, which Delta Green Structure specializes in integrating). Durability & Low Maintenance: A well-designed and constructed LGSF building, protected by appropriate cladding and finishes, offers exceptional long-term durability with minimal maintenance required, unlike structures prone to water damage or pest infestation. Delta Green Structure: Best LGSF constructor in West Bengal As a local LGSF manufacturer based in West Bengal, Delta Green Structure isn’t just selling steel frames; we’re providing peace of mind. We deeply understand the unique environmental challenges our state faces – the cyclone paths, the seismic zones, the floodplains. This local knowledge is integrated into our solutions. At Delta Green Structure, we are committed to empowering homeowners, businesses, and communities across our state with this advanced building technology. By choosing LGSF, you’re not just constructing a building; you’re investing in a fortress designed to protect lives, property, and the continuity of your business or family life when disaster strikes. It’s the smart, responsible choice for building a safer, more resilient West Bengal. Ready to build stronger? Contact Delta Green Structure, your trusted LGSF manufacturer in West Bengal, today to discuss how we can help you create a truly disaster-resistant future.
The Role of LGSF in Disaster-Resistant Buildings Read More »